Introduction
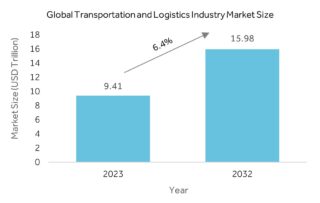
The global transportation and logistics industry is experiencing significant growth. In 2023, the market was valued at ~ USD 9T, with projections suggesting an expansion to ~USD 16T by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of ~6.4%. This backdrop of robust economic activity sets the stage for a transformative era in the industry, driven by the rapid evolution of technology.
 As global commerce expands and consumer expectations rise, the sector is leveraging cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and reduce environmental impacts. These innovations are not only addressing current challenges but are also setting the stage for future growth by integrating digital solutions that improve connectivity, visibility, and responsiveness within global supply chains.
As global commerce expands and consumer expectations rise, the sector is leveraging cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and reduce environmental impacts. These innovations are not only addressing current challenges but are also setting the stage for future growth by integrating digital solutions that improve connectivity, visibility, and responsiveness within global supply chains.
Imagine a world where drones deliver your parcels, real-time tracking of your shipments is the norm, and artificial intelligence orchestrates logistics operations with impeccable precision. This scenario isn’t a glimpse into a far-off future but a vivid portrayal of today’s transportation and logistics landscape. Technology has been playing a crucial role in addressing the needs driven by growing global trade and evolving consumer behavior and preferences. From the integration of AI to the deployment of IoT, let’s delve into the technological breakthroughs that are rendering logistics and transportation operations faster, smarter, and more environmentally sustainable.
This article delves into the five transformative technology trends currently revolutionizing the transportation and logistics sectors, exploring how they catalyze significant improvements in service delivery, cost management, and environmental stewardship while anticipating the future needs of a rapidly changing industry landscape.
1. Transforming Logistics with IoT and Advanced Data Analytics:
In the rapidly evolving world of logistics, the integration of IoT and advanced data analytics is transforming the landscape. The use of data-driven decision-making forms the backbone of modern logistics networks, leveraging robust data collection and analysis to sharpen precision and efficiency. As per Future Market Insights, the global IoT spend by the logistics industry is estimated at USD 39.6 Bn in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 114.7 Bn by 2032 recording a CAGR of 11.2%. This technological evolution is powered by IoT devices, sensors, and advanced tracking systems seamlessly integrated within infrastructure and vehicles. These systems are pivotal in collecting real-time data from various sources such as vehicle locations, cargo conditions, traffic patterns, and weather forecasts.
A prime example of this innovation is the use of smart cold chains, where containers are equipped with sensors that collect real-time data about conditions inside the container to monitor the temperature and humidity of the storage in real-time and transmit it over the internet. The collected data is analyzed to assess the safety and quality of the products, and if any anomalies are detected, alerts can be sent out immediately to take corrective measures.
2. Enhancing Efficiency and Safety with Automation, Robotics, and Intelligent Systems:
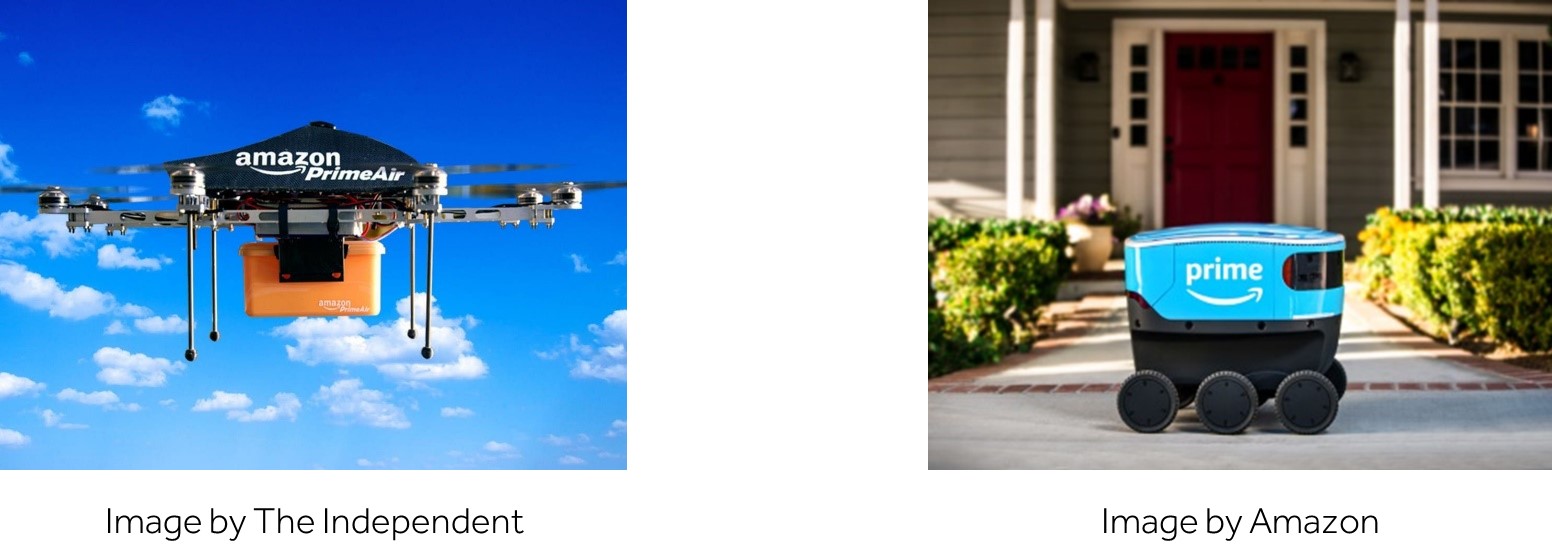
Automation and robotics are at the forefront of transforming logistics operations. From automated warehouses equipped with robotic picking systems to drones delivering packages, these technologies are reducing labor costs, increasing accuracy, and speeding up service delivery. For example, Amazon’s deployment of drones and robots in their fulfillment centers and delivery systems exemplifies how these technologies are revolutionizing service delivery and operational efficiencies. Automation extends to autonomous vehicles, such as self-driving trucks, which improve safety and efficiency while reducing human fatigue and errors. AI and machine learning algorithms integrated into transportation management systems have been proven to save logistics companies up to 20% on transportation costs. These intelligent systems analyze vast amounts of data to optimize routes, predict maintenance, and enhance fleet management. Advanced communication technologies like V2V (vehicle-to-vehicle) and V2I (vehicle-to-infrastructure) facilitate real-time information sharing, significantly boosting overall efficiency and safety.

3. Greening the Supply Chain with Sustainable Practices:
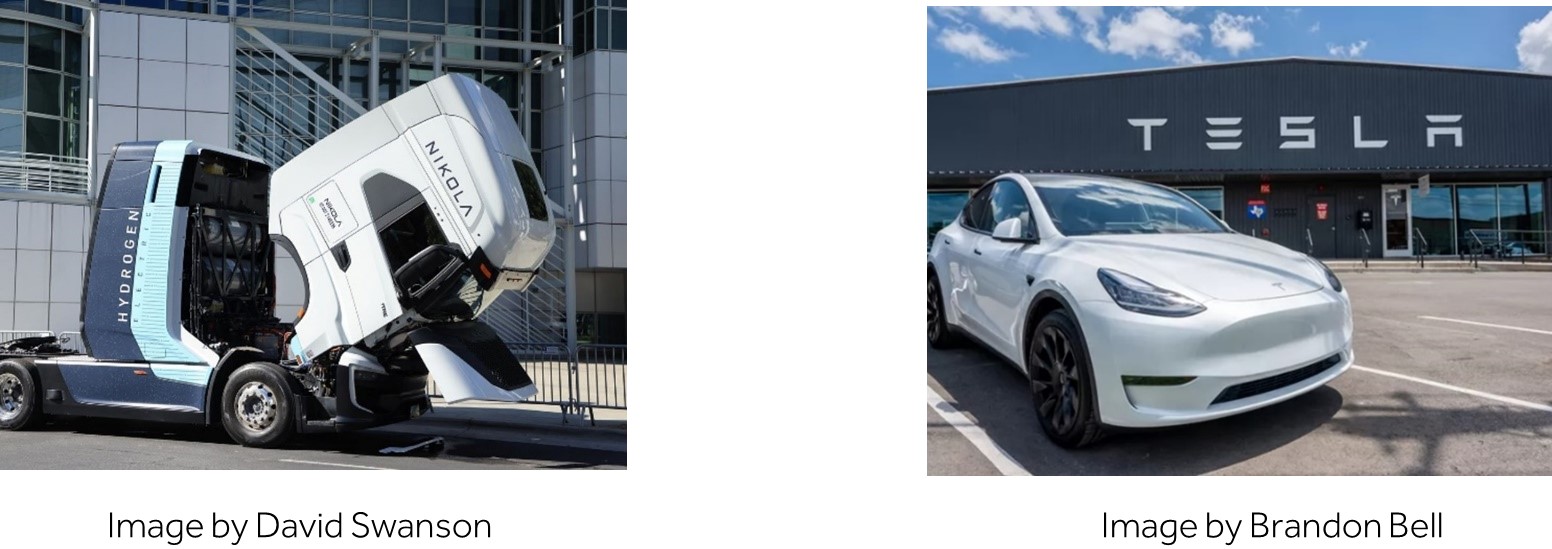
As environmental concerns intensify, the logistics industry is increasingly turning towards sustainable technologies. The global electric truck market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 21% from 2019 to 2024. Electric and hydrogen-fuel vehicles are becoming more prevalent, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of transportation. Moreover, advancements in energy-efficient warehousing and renewable energy sources underscore the industry’s commitment to reducing environmental impacts. Leading companies like Tesla and Nikola are at the forefront of integrating these sustainable solutions. For instance, Nikola’s hydrogen-powered fuel cell electric vehicles that are designed for longer or continuous metro-regional applications, exemplify this trend by offering a maximum range of up to 500 miles with 0 tailpipe emissions. This significantly contributes to reducing the environmental footprint of logistics operations.

4. Increasing Transparency and Operational Flexibility with Digital Twins and Blockchain:
Digital twins represent a revolutionary leap in logistics planning and execution. These virtual replicas of physical assets or systems are updated with real-time data, allowing companies to model, simulate, and optimize their operations virtually before implementing changes in the real world. For instance, DHL Supply Chain creates digital twins of its warehouses, which serve as virtual replicas of the physical facilities. These digital twins accurately capture the layout, inventory, equipment, and operational processes within the warehouses, enhancing operational flexibility and resilience, especially in complex logistical scenarios. Blockchain technology is increasingly recognized for its potential to enhance transparency and security within the supply chain. By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger of all transactions, blockchain enables unparalleled traceability of goods from origin to delivery. This transparency helps combat fraud, streamline operations, and foster trust among stakeholders, including suppliers, shippers, and consumers
5. Transforming Training and Customer Experiences with AR, VR, and Cloud Technologies:
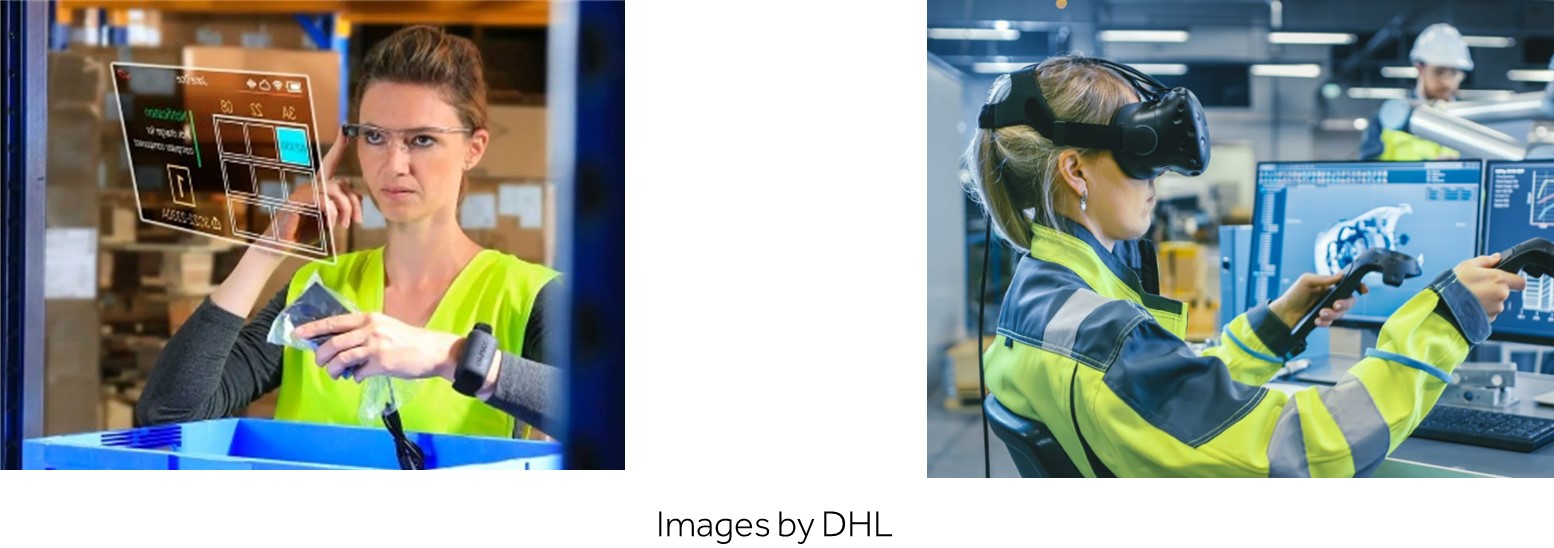
AR and VR are transforming logistics training and operations. AR glasses provide real-time guidance to warehouse workers, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in picking processes, while VR offers a risk-free environment for comprehensive training, allowing employees to practice various operational scenarios safely. Cloud technologies complement these innovations by enabling seamless data sharing and collaboration across global networks. Companies like DHL are leveraging AR to improve picking accuracy, ensuring faster and more efficient deliveries. Additionally, cloud-based Transportation Management Systems (TMS) support route optimization, freight brokerage, real-time inventory management, and enhanced customer service, making logistics operations more integrated and responsive. This combination of advanced technologies supports everything from daily logistical tasks to strategic decision-making, fundamentally changing how logistics networks operate.

Conclusion
The technological evolution in the transportation and logistics sectors is rapid and revolutionary, driven by a relentless pursuit of efficiency, enhanced safety, and a reduced environmental footprint. As these technologies continue to mature and integrate, they promise to unlock new levels of performance and innovation. The future of logistics is here, characterized by a seamless blend of digital and physical operations that reshape how the world connects and conducts business. The road ahead is not just about adapting to change but embracing and leading it, ensuring that logistics operations are not only efficient but also resilient, sustainable, and prepared for the demands of tomorrow.
References:
- FedEx (2024)
- Commercial Construction Renovation (2024)
- Research and Markets (2023)
- The Code Work (2023)
- Amazon (2023)
- Quartz (2023)
- Unipart Logistics (2023)
- Legacy Supply Chain (2023)
- Yoh (2023)
- IBM (2022)
- Supply Chain Management Review (2022)
- ING (2021)
- TechTarget (2020)
- DHL (2019)



