The Rise of Digital Twin Technology
In recent years, digital twin technology has gained significant momentum across various industries, transforming the way organizations design, operate and maintain complex systems. While the concept originated in the early 2000s, its prominence has surged in recent years as part of the broader adoption of AI, Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization of physical systems.
Today, digital twin technology stands at the forefront of widespread adoption, with the global market projected to grow at an annual rate of 60%, reaching an estimated $73.5 billion by 2027. Additionally, around 70% of C-suite technology leaders at large enterprises are actively exploring and investing in this transformative technology. As organizations increasingly recognize its potential to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance, digital twin technology is poised to redefine industry standards and unlock new possibilities for innovation.
Understanding Digital Twin Technology and Digital Twin of Customers (DToCs)
A digital twin is a “virtual counterpart” that captures real-time data to replicate the behavior, preferences, and needs of a physical object, system, or individual. Digital twins have found applications in a wide range of industries primarily for optimizing physical assets such as products or systems. However, there is increasing interest in leveraging this technology to enhance customer experience through the emerging concept of the Digital Twin of a Customer (DToC).
DToCs create a comprehensive, data-driven representation of an individual customer, capturing the customer’s preferences, habits, and interactions, enabling businesses to anticipate future needs, predict behaviors, and deliver personalized experiences. This not only enhances customer satisfaction and retention, but also drives more informed decision-making, optimized marketing strategies, and increased sales.
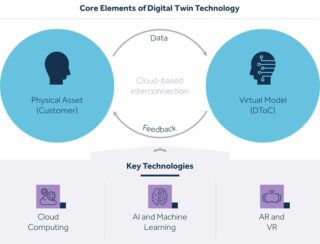
Operationally, digital twin technology is driven by three core elements: a physical entity (e.g. product, system, individual), a virtual model that represents it, and a data connection that continuously updates the virtual model with real-time information. The physical entity is equipped with sensors and devices that captures real-time data, which is then transmitted to the virtual model. The virtual model, created using advanced modeling techniques like computer-aided design (CAD) or building information modeling (BIM), mirrors the physical entity’s structure and behavior, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive analysis. The system relies on key technologies such as cloud computing for processing and storing data; AI, machine learning to enable simulation models; and AR and VR to enable visualization and interactions between the virtual model and physical system. Together, these components create a feedback loop that enhances understanding, optimization, and decision-making, leading to improved performance and cost efficiency.
Reshaping Customer Experience with DToCs: Use Cases Across Industries
DToCs have been successfully deployed across various industries, providing several use cases that demonstrate the wide range of benefits for organizations.
1. Retail
In the retail sector, DToCs are improving customer engagement by allowing retailers to gain a deep understanding of customer preferences, shopping habits, and purchase history. This data helps businesses deliver personalized shopping experiences, recommendations, and targeted marketing campaigns. For example, Amazon utilizes DToCs to offer product recommendations based on customers’ past purchases and browsing behavior, using generative AI to refine suggestions and highlight key products. Amazon’s recommendation engine is responsible for approximately 35% of its total sales, demonstrating the significant impact of personalized recommendations.
Beyond customer personalization, digital twins can enhance in-store shopping experiences by incorporating technologies like motion sensors and smart drawers to track customer movement and purchasing patterns. For example, home improvement retailer Lowe, implemented digital twin technology to optimize store layouts by combining spatial data, real-time sensor inputs, and AR technology. Their system enables staff to visualize shelves in 3D, restock efficiently with AR overlays, and analyze customer movement to improve product placements.
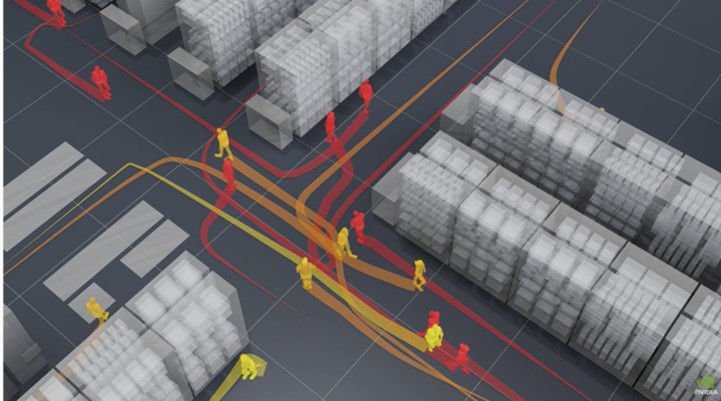 Use of digital twin technology in Lowe’s store to simulate customer traffic flow patterns trained on historical data (Source: Lowe’s Innovation Labs)
Use of digital twin technology in Lowe’s store to simulate customer traffic flow patterns trained on historical data (Source: Lowe’s Innovation Labs)
2. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, DToCs are revolutionizing patient care by enabling healthcare providers to create data-driven replicas of individual patients based on medical records, genomic data, lifestyle choices, and treatment histories. These digital twins enable physicians to deliver personalized care, leveraging predictive analytics to anticipate health risks, design tailored treatment plans, and implement preventive measures. For example, Twin Health, a health technology company, has developed the “Whole Body Digital Twin”, a real-time model of an individual’s unique metabolism, which uses AI to analyze over 3,000 daily data points, offering precise recommendations to improve patient outcomes. According to Twin Health, patients who have used the technology for over a year, experienced over 70% of medications eliminated, reduced inflammation, and improved insulin resistance (in those with type 2 diabetes).
3. Financial Services
In the financial sector, DToCs are being used by institutions to understand customer behavior, manage risks, and optimize operations. By creating real-time digital replicas of customers, DToCs analyze transaction patterns, spending habits, and income stability, providing insights into financial behavior. This enables banks to deliver personalized services, such as tailored product recommendations, proactive customer support, and automated risk assessments for credit evaluations and loan approvals. For example, Citibank leveraged DToCs and AI-driven analytics to scan vast amounts of customer data, helping predict financial behavior and personalize banking experiences. By integrating AI with its digital twin framework, Citibank offers tailored financial products, such as travel-related loan recommendations when a customer books a flight. This approach has also improved fraud detection, security, and digital banking efficiency, reinforcing Citibank’s strategy to optimize customer interactions through predictive insights.
Operationally, DToCs can enhance branch efficiency and optimize staff allocation by analyzing real-time customer flow and service demand. For example, when Bank of Montreal (BMO) acquired Bank of the West’s 503 branches in 2023, it used spatial-mapping technology to create 3D digital twins of all the branch locations to complete remote site assessments and operational tests without service disruptions. The simulations helped BMO evaluate branch layouts and enhance space utilization, ensuring a smooth transition while maintaining service standards.
4. Telecommunications
In the telecommunication sector, network providers use DToCs to create real-time digital replicas that represent individual subscribers and their interactions with the network. These digital twins analyze customer behaviors, usage patterns, and preferences, allowing telecom companies to deliver tailored recommendations, proactive troubleshooting, and targeted marketing campaigns. For example, Ericsson used NVIDIA’s Omniverse to create digital twins for both 5G subscribers and radio wave propagation, leveraging advanced simulation tools to model real-time interactions between users and the network. These simulations accounted for factors like user mobility, bandwidth usage, and radio frequency propagation within different environments, such as urban settings and indoor spaces. By optimizing resource allocation, predicting network congestion, and analyzing signal performance, Ericsson improved service quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and reduced operational costs, showcasing the transformative potential of digital twins in advancing 5G technology.
Ericsson’s 5G Digital Twin Simulated in NVIDIA Omniverse (Source: NVIDIA)
Challenges and Limitations in Implementing Digital Twin Technology
While digital twin technology offers significant benefits, its implementation comes with various complexities that organizations must navigate, namely:
1. Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating digital twins with outdated hardware or siloed software in existing infrastructure can be challenging, as these older systems may not support modern digital twin technologies.
2. Data Quality and Availability
The effectiveness of digital twins heavily relies on accurate and complete data. Poor data quality or lack of availability can compromise their reliability and overall performance.
3. Cybersecurity Risks
Digital twins centralize sensitive data and system controls, making them more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ensuring robust security measures is crucial to protecting these systems from potential threats.
4. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The vast amount of user data collected and analyzed by digital twins raises concerns about privacy and ethics. Proper regulations and safeguards must be in place to ensure responsible data usage.
5. Stakeholder Management
The successful adoption of digital twins depends on the commitment and engagement of key stakeholders. A lack of support or interest from stakeholders can slow down or even prevent implementation.
Looking to the Future
DToCs are transforming how businesses across industries engage with their customers by offering unparalleled insights and personalization. Across various industries, DToCs enable businesses to predict customer needs, enhance efficiency, and offer customized experiences. However, successful implementation requires addressing various challenges such as integration with legacy systems, data quality, and cybersecurity risks. As technology advances, the potential of DToCs will continue to grow, empowering organizations to innovate and adapt in an increasingly competitive landscape. By leveraging these dynamic, data-driven tools, businesses can create deeper relationships with customers, reduce costs, and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving digital world, setting a new standard for customer engagement.
References:
- Binmile (2025)
- Intersect Technologies (2025)
- TwinHealth (2025)
- Toobler (2025)
- McKinsey & Company (2024)
- Delve AI (2024)
- Amazon (2024)
- Remsense (2024)
- Rebuy (2024)
- Galaksiya (2024)
- Lowe’s Innovation Lab (2024)
- Stellarix (2024)
- Pymnts (2024)
- Banking Journal (2024)
- Engineering (2024)
- Jolan Paauw (2023)
- Pathmonk (2023)
- IoT Analytics (2023)
- PwC (2022)
- Boston Consulting Group (2022)
- Ericsson (2022)
- IBM (2020)
Related articles

Top LLMs Global Distribution by Country Market Share

MENA’s Innovative Solutions to Water Scarcity


