Introduction
Healthcare has always been at the forefront of technological innovation. From the introduction of wearable technology to the rise of artificial intelligence, technology has fundamentally transformed the way healthcare is delivered. Today, digital technologies are not just supporting tools but integral components of modern healthcare systems. Therefore, the use of technology in healthcare has become increasingly popular in recent years, with the potential to improve healthcare delivery, patient outcomes, and cost-effectiveness while transforming patient care and operational efficiency through innovative solutions. This article explores the utilization of technology in healthcare, highlighting its landscape, benefits, and challenges, along with its future expectations.
Healthcare Technology Landscape
Key areas of utilization include artificial intelligence, telemedicine, wearable health monitors, and robotic surgery, enhancing the provision of healthcare services to promote a more convenient and seamless experience for patients and healthcare service providers.
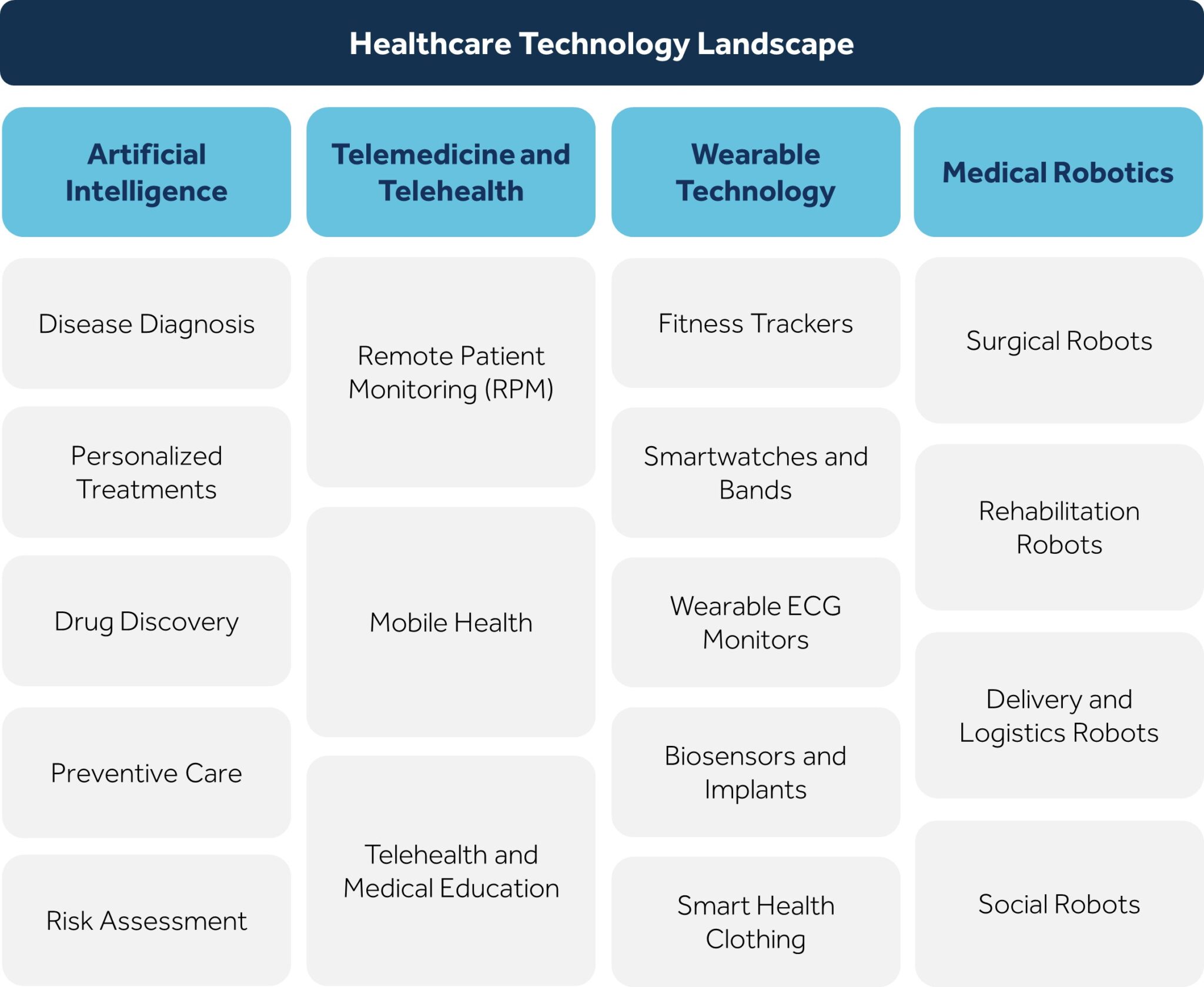
Artificial Intelligence
The healthcare AI market is rapidly growing, driven by increased investments from both government and private sectors. According to a study by PwC, the global artificial intelligence market in healthcare was valued at USD 11 billion in 2021 and is expected to surge to USD 188 billion by 2030. Countries like China, South Korea, and India are significantly investing in AI technologies to improve healthcare outcomes and accessibility.
There are many applications for AI in healthcare, such as drug discovery where it is used to analyze medical datasets, identify genetic mutations, and optimize drug candidates, ultimately accelerating the process and improving success rates. Additionally, AI is used in personalized treatment to analyze patient data and suggest tailored options, while also enhancing disease detection and diagnostics by building decision-support systems, reading medical scans, predicting cancer recurrence, and analyzing medical samples.
Forecasted market size for AI in healthcare worldwide from 2021 to 2030
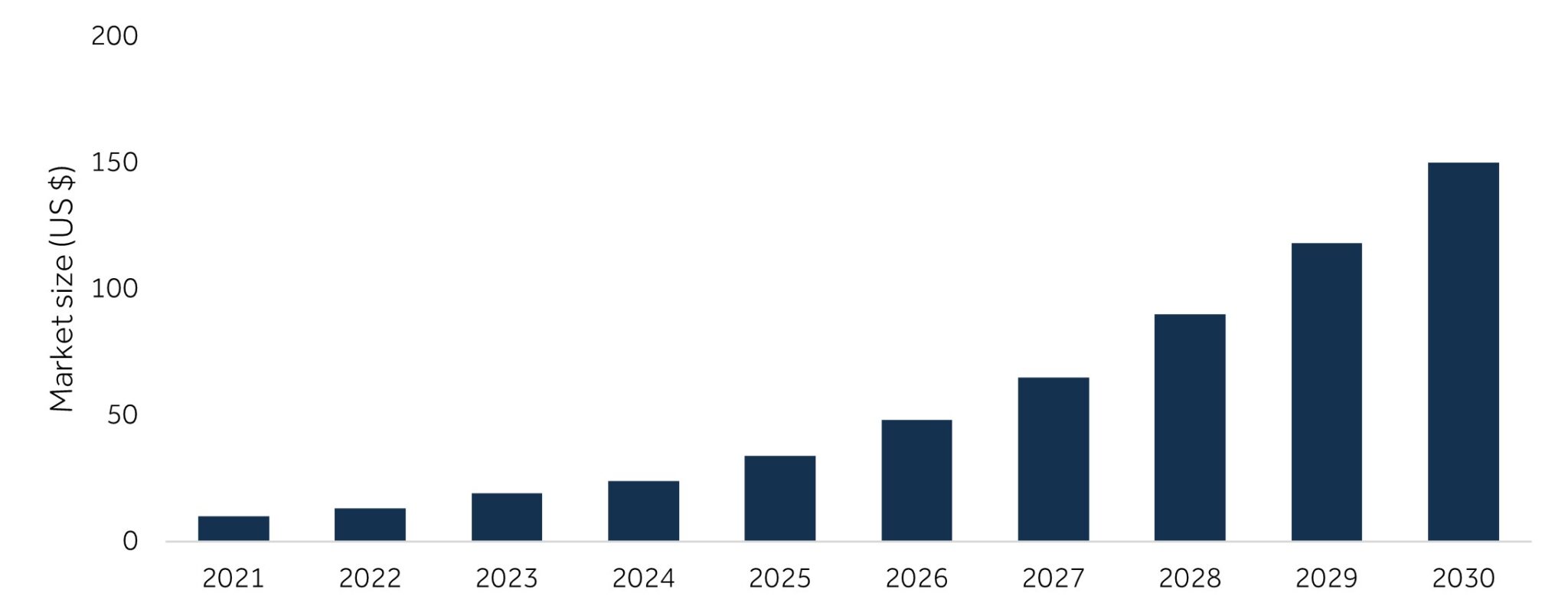 Fig. 1: Estimated Global Healthcare AI Market Value 2021-2030 (PWC, 2023)
Fig. 1: Estimated Global Healthcare AI Market Value 2021-2030 (PWC, 2023)
Telemedicine and Telehealth
Telemedicine and Telehealth have revolutionized healthcare by using digital technologies to provide remote care, significantly expanding access and convenience for patients. Initially slow to gain traction, these services saw rapid adoption during the COVID-19 pandemic, transforming the healthcare landscape. According to an article by J.P. Morgan, the global telehealth market was valued at USD 83.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 24% from 2023 to 2030. As digital ecosystems evolve, they promise to deliver seamless, integrated healthcare experiences, consolidating various services into user-friendly platforms.
One of the most crucial examples of telemedicine and telehealth is Remote Patient Monitoring, which allows healthcare providers to manage acute and chronic conditions by monitoring certain aspects of a patient’s health from their home, reducing travel costs and infection risk. Additionally, Mobile Health focuses on proactive health concepts such as nutrition and wellness, improving care efficiency, and enabling patient education and self-management.
Wearable Technology
Wearable technology offers innovative solutions for monitoring and managing health, enhancing patient outcomes through real-time data collection and analysis.
According to an industry report by Fortune Business Insights, the wearable healthcare devices market size globally was estimated to be worth USD 157.9 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.4 trillion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 31.5% from 2024 to 2032.
Wearable technology includes several uses, such as Fitness Trackers which are used to monitor and record various physical activities and health data, including steps taken, distance traveled, calories burned, and heart rate; Smart Watches are versatile devices that can be used as workout companion and help track health among other things; and Biosensors, which are analytical devices used for the detection of a chemical substance, playing a critical role in fields like biomedical diagnosis, monitoring of treatment and disease progression, drug discovery, food control, and environmental monitoring.
Medical Robotics
Medical robotics involves the use of robotic systems to perform complex surgical procedures, enhancing precision, flexibility, and control in minimally invasive surgeries. A KPMG study showcases the global market’s expected growth from USD 10.6 billion in 2021 to USD 35 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 14.2%, driven by substantial investments in robotic surgery companies. This rapid advancement and adoption of medical robotics are set to revolutionize patient care, improving outcomes and expanding the capabilities of modern medicine.
Medical robotics includes surgical robotics, which enhances precision and control in complex procedures, and rehabilitation robotics, which uses robotic devices to assist inpatient rehabilitation and sensorimotor function recovery.
Benefits of Utilizing Technology in Healthcare
Enhanced Access and Quality of Care
Technology enables remote consultations and telemedicine, making healthcare more accessible to underserved populations. It allows real-time access to patient data, which improves decision-making among healthcare providers. This fosters better collaboration and enhances patient outcomes by providing timely and accurate medical interventions.
Empowered Patient Engagement and Self-Management
Technology empowers patients by providing them access to their health information and enabling them to monitor their status. Patients can participate actively in their care processes, leading to better health outcomes. Increased engagement through digital tools helps patients manage chronic conditions and adhere to treatment plans more effectively.
Operational Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
The automation of administrative tasks and streamlining of processes reduce operational costs and administrative burdens. This efficiency results in faster service delivery and better resource allocation, ultimately improving the quality of patient care. By minimizing manual work, healthcare providers can focus more on patient-centric activities.
Revolutionized Treatment Approaches with Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics and personalized medicine, driven by IT capabilities, are transforming treatment approaches. Big data and machine learning provide insights for personalized treatment plans, ensuring more accurate diagnoses and tailored interventions. This optimizes patient recovery and supports long-term health management through precise and individualized care strategies.
Challenges of Utilizing Technology in Healthcare
Data Privacy and Security
As patient information becomes increasingly digitized and interconnected, protecting it from breaches and cyber threats remains a vital concern. Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive health data is crucial to maintaining patient trust and complying with legal requirements.
Lack of Standardization
The lack of standardization across various technology systems complicates data sharing and communication between healthcare providers. This inconsistency can lead to errors in medical decision-making and hinder the seamless integration of healthcare technologies.
Human Factors
Varying levels of user acceptance among patients and healthcare professionals influence the successful adoption of technological solutions. Resistance to change, lack of training, and differing comfort levels with technology can impact the effectiveness of these solutions.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Navigating stricter data privacy laws and ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI and machine learning adds complexity for healthcare organizations. Compliance with legal and regulatory standards is essential to avoid legal repercussions and ensure ethical use of advanced technologies in healthcare.
Future Expectations for Healthcare Technology
Healthcare is set to transform dramatically with new technologies. A key change will be in how health information is managed, giving individuals more control over their data through secure online platforms. This shift from centralized to personal data storage will enhance privacy and empower people in the use of their data.
Furthermore, advancements such as improved computer interfaces and wearable gadgets will play a significant role in healthcare. These innovations will aid in collecting more health data and make it easier to monitor health remotely. Additionally, artificial intelligence and machine learning will utilize this data to enhance disease diagnosis and treatment, resulting in more personalized and effective healthcare. Technologies like virtual reality and robots would be used more in healthcare, expanding the reach of medical care beyond hospitals, making it possible to provide more services in homes and communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of technology in healthcare has brought about transformative changes, enhancing patient care, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. From Artificial Intelligence to wearable technology and medical robotics, these innovations promise a future where healthcare is more focused on people, utilizing technology to offer better care, prevent illnesses, and make healthcare more accessible to everyone. Despite the challenges of data privacy and standardization, the continued advancements in healthcare technology are positioned to further revolutionize the industry. The focus will increasingly be on leveraging these technologies to provide better, more efficient, and patient-centered care in the years ahead.
References
- Fortune Business Insights (2024)
- Debnath, S. (2023)
- KPMG (2023)
- PWC (2023)
- Singh, J. (2023)
- Stolzfuz, M. & Kaur, A. (2023)
- J.P. Morgan (2022)
- McKinsey & Company (2020)




