Evolution of Robo-Advisors Globally
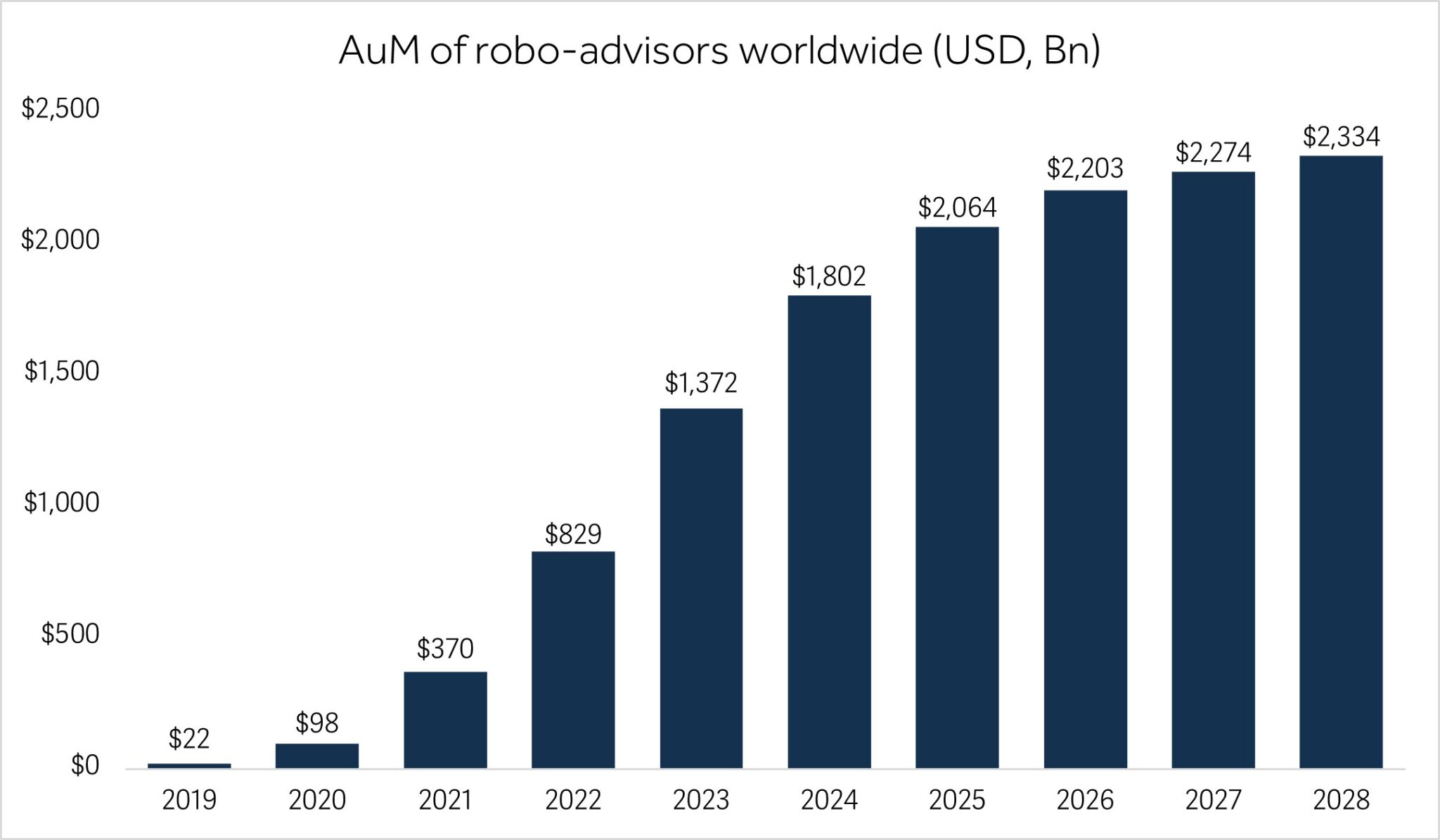
In the evolving landscape of wealth management, robo-advisors have emerged as a significant force, transforming how investment advice and portfolio management services are delivered. These automated platforms utilize algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) to offer personalized financial guidance at a fraction of the cost of traditional advisory services. Globally, the adoption of robo-advisors has surged, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Assets under management (AUM) by robo-advisors worldwide are projected to reach $2.33 trillion by 2028, up from $1.37 trillion in 2023.
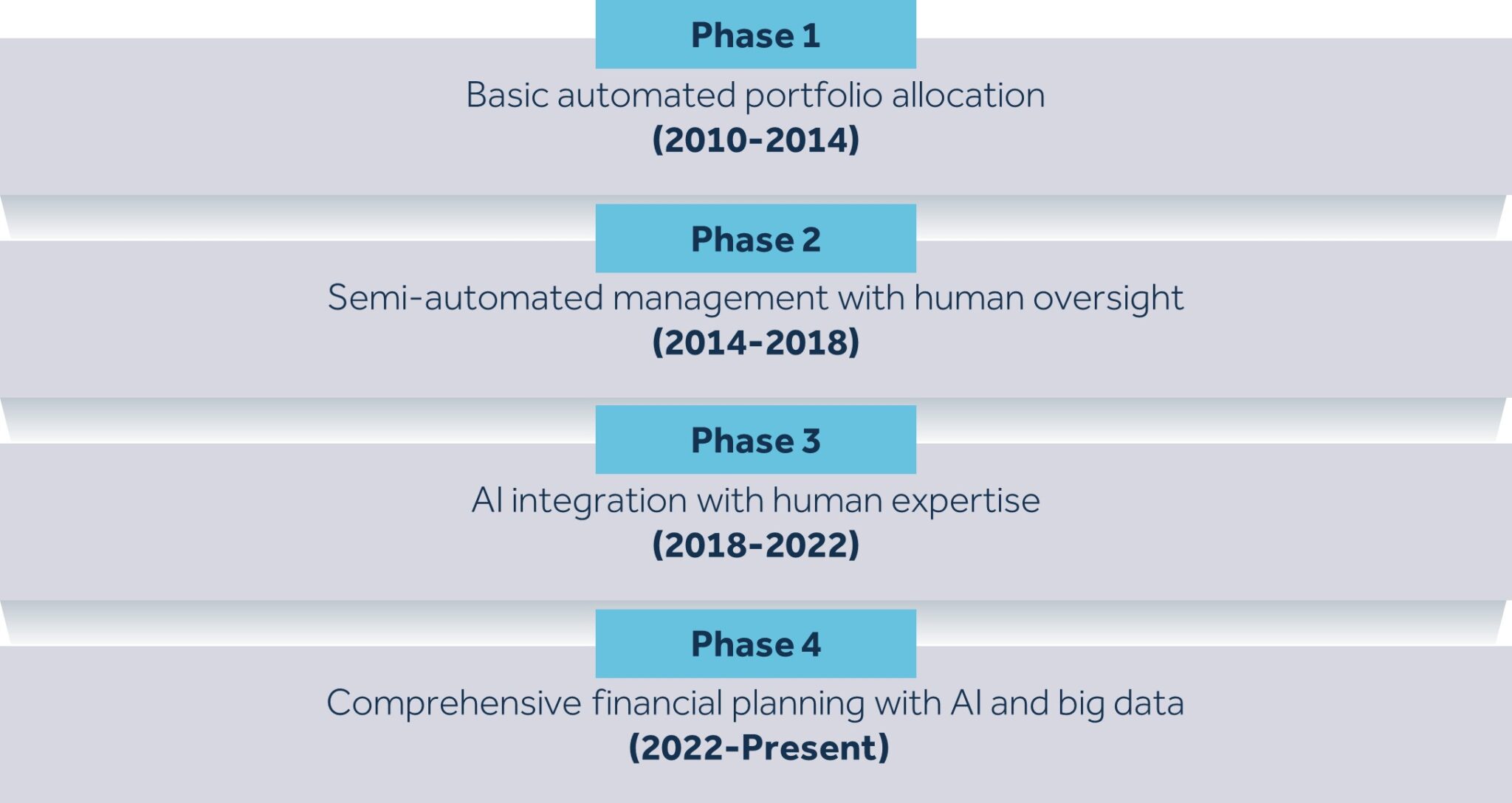
 Evolution of Robo-Advisors from Phase 1.0 to 4.0
Evolution of Robo-Advisors from Phase 1.0 to 4.0
Robo-Advisor 1.0: Initial Phase of Algorithmic Investing
The evolution of robo-advisory services, often called Digital Wealth Management, has progressed through distinct phases from 1.0 to 4.0. Initially, in its 1.0 phase, robo-advisors focused on basic automated portfolio allocation using algorithms, providing cost-effective investment choices compared to traditional advisors. After completing a questionnaire, clients were presented with recommendations for individual products or portfolio allocations determined by selected investment choices. They were responsible for independently purchasing and managing actual portfolios using their accounts, including making future adjustments. Offerings encompassed a range of products such as stocks, bonds, ETFs, and other investment vehicles.
Robo-Advisor 2.0: The Era of Semi-Automated Management
Moving into the 2.0 phase, robo-advisor platforms significantly improved user experience by offering more personalized investment advice and a broader array of investment choices, accommodating a wide range of investor profiles. These platforms structured investment portfolios as diversified funds of funds, providing comprehensive services that included establishing investment accounts and executing direct transactions on behalf of clients. Dedicated investment managers played a pivotal role by using questionnaires not only to filter suitable investment products but also to allocate clients to a curated selection of risk-adjusted portfolios tailored to their financial goals and risk tolerance.
During this phase, the implementation process became semi-automated, with investment managers overseeing sophisticated investment algorithms and establishing rules for asset allocation and portfolio management. This approach combined the efficiency of automated systems with the oversight and expertise of human managers, ensuring that investment strategies were aligned with client objectives while leveraging technological advancements to optimize performance and minimize risk.
Robo-Advisor 3.0: Combining AI with Human Expertise
In the 3.0 phase, robo-advisors advanced by integrating cutting-edge technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). These innovations enabled them to enhance portfolio management capabilities significantly, providing real-time market insights and implementing proactive rebalancing strategies. Investment decisions and proposals for portfolio adjustments were driven by sophisticated algorithms meticulously designed to monitor and execute predefined investment strategies with precision and efficiency.
While algorithms played a pivotal role in automating these processes, oversight remained crucial and was provided by seasoned fund managers who ensured strategies aligned with client objectives and market conditions. This dual approach combined the computational power of AI with human expertise to optimize investment outcomes.
Moreover, some platforms empowered clients with the flexibility to customize their investment portfolios according to their preferences. They could choose to follow or diverge from automated portfolio adjustment recommendations, enabling a tailored approach that met individual financial goals and risk tolerances effectively. This level of customization reflected the evolving nature of robo-advisory services towards more personalized and responsive financial management solutions.
Robo-Advisor 4.0: Intelligent and Holistic Wealth Management
Currently, in the 4.0 phase, the focus is on comprehensive financial planning, including goal-based investing, tax optimization, and holistic wealth management solutions. This evolution underscores a shift towards more intelligent, user-centric platforms that leverage big data and AI to deliver increasingly personalized and effective financial advice.
Advanced risk management and client profiling questionnaires facilitate direct investments through AI-driven investment algorithms that continuously learn and adapt. These algorithms dynamically allocate assets across various classes based on evolving market conditions and individual investment objectives, including profit goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity requirements. They actively monitor and adjust client portfolios in real-time to maintain alignment with selected investment strategies.
Global Trends in Robo-Advisors
The landscape of robo-advisors is constantly advancing, shaped by technological advancements, regulatory developments, and shifting investor preferences worldwide. This section explores key global trends driving the evolution of robo-advisory services in wealth management, highlighting their impact on financial markets and the broader economy. From advancements in artificial intelligence to regulatory adaptations and changing investor behaviors, these trends underscore the transformative potential of robo-advisors in reshaping how wealth management services are accessed and delivered globally.
Increased Digitalization
The financial services industry is rapidly embracing digital solutions, with consumers preferring the convenience and accessibility of online platforms. Robo-advisors fit seamlessly into this digital shift, offering 24/7 access and user-friendly interfaces. This trend towards digitalization is not just a shift in technology but also a cultural change, as more individuals trust and rely on digital tools for financial management.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital services across industries, including wealth management. As traditional face-to-face advisory services were disrupted, the demand for remote financial management tools surged, highlighting the efficiency and convenience of robo-advisors. These platforms enabled users to manage their investments seamlessly from anywhere, ensuring continued access to financial advice and portfolio management without the need for physical interactions.
Cost Efficiency
Traditional wealth management services typically come with high fees, encompassing management, advisory, and transaction costs. In contrast, robo-advisors utilize automation to deliver comparable services at a reduced cost, expanding access to financial advice across a wider demographic. This affordability is especially attractive to younger investors and individuals with smaller portfolios, who may find traditional advisors’ high minimum investment thresholds prohibitive.
The competitive pricing strategies of robo-advisors have prompted traditional wealth management firms to reevaluate their fee models. Many are adapting by introducing hybrid approaches that integrate automated tools with personalized human advice, aiming to maintain competitiveness in an evolving financial advisory landscape.
Personalization and Customization
Modern robo-advisors utilize sophisticated algorithms to tailor investment strategies to individual client needs, considering factors such as risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizons. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to provide personalized recommendations that would be time-consuming and expensive for human advisors to match.
For instance, some robo-advisors use machine learning to continuously improve their investment strategies based on historical data and market trends. This level of personalization ensures that clients receive advice closely aligned with their financial objectives and risk appetite.
Integration of ESG Factors
As investors become more socially conscious, many robo-advisors now incorporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into their investment models. This trend aligns portfolios with clients’ ethical values and meets the growing demand for sustainable investing options. Robo-advisors can easily integrate ESG criteria into their algorithms, allowing users to invest in companies and funds that adhere to specific ethical standards. This integration not only caters to socially responsible investors but also attracts younger demographics who prioritize sustainability in their investment choices.
Challenges and Opportunities
As we explore robo-advisory services in wealth management, it’s clear their potential is vast, yet several significant challenges must be tackled. These include building trust in digital financial services, enhancing financial literacy, adapting regulatory frameworks, ensuring robust cybersecurity, and addressing infrastructural barriers. Successfully navigating these hurdles is essential to fully realizing the benefits of robo-advisory services.
Trust and Cultural Preference
Trust remains a critical issue, as investors traditionally prefer face-to-face interactions. Many individuals are accustomed to personalized service and may be hesitant to rely on automated platforms for financial advice. Building trust requires demonstrating the reliability, security, and effectiveness of robo-advisors through transparent operations and strong regulatory frameworks.
Cultural preferences also play a role in the adoption of financial services. Some investors may prefer dealing with human advisors who understand their unique cultural and financial needs. Robo-advisors must find ways to bridge this gap, potentially through hybrid models that combine automated advice with human interaction.
Financial Literacy
Financial literacy levels vary widely, necessitating robust educational initiatives to ensure investors fully understand and trust automated financial services. Providing clear and accessible information about how robo-advisors work, the benefits they offer, and the risks involved is essential for promoting adoption.
Educational campaigns can include workshops, online resources, and collaboration with schools and universities to improve financial literacy. By empowering individuals with knowledge, robo-advisors can build a more informed and confident client base.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape for robo-advisors varies significantly across jurisdictions, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Regulators worldwide are adapting frameworks to accommodate fintech innovations, including robo-advisory services. However, complexities and fragmentation often require harmonization to support consistent growth and ensure investor protection.
Regulations typically address investor protection, algorithmic transparency, data privacy, and cybersecurity. In the European Union, for example, regulations such as the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) impose stringent standards on financial services and data handling, promoting transparency and safeguarding consumer rights.
In the United States, robo-advisors are overseen by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which mandates registration, disclosure of algorithms, and adherence to fiduciary duties. This regulatory approach aims to balance innovation with investor protection, fostering trust and market integrity.
As technological advancements continue, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve to address emerging risks and ensure that robo-advisory services remain accessible, secure, and aligned with investor expectations. Improved regulatory clarity will play a pivotal role in expanding the role of robo-advisors in democratizing access to sophisticated financial advice globally.
Conclusion
Robo-advisors have emerged as transformative tools within the global wealth management industry, redefining how investment advice is accessed and managed. Their evolution from basic portfolio allocation to sophisticated, AI-driven financial planning reflects a paradigm shift towards efficiency, personalization, and accessibility. With assets under management projected to grow significantly, robo-advisors are poised to democratize financial services, particularly appealing to digital natives and cost-conscious investors.
Despite their potential, several challenges such as building trust, enhancing financial literacy, and navigating regulatory landscapes persist. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial in realizing the full potential of robo-advisory services. Efforts to foster transparency, cybersecurity, and regulatory harmonization are essential to bolstering investor confidence and adoption rates.
Looking forward, partnerships between traditional financial institutions and fintech firms present opportunities to expand market reach and enhance service offerings. Tailoring robo-advisory solutions to local market dynamics and cultural preferences will further drive adoption and sustainability.
As the fintech ecosystem continues to evolve, robo-advisors are well-positioned to lead the digital transformation of wealth management globally. By leveraging technological advancements and adapting to changing consumer behaviors, they promise to deliver increasingly personalized and effective financial solutions, ensuring broader access to sound investment strategies for all.
References:
- DIFC Innovation Hub (2024)
- Statista (2024)
- TAZI (2024)
- VastAssembly (2024)
- Riyadh Valley Co. (2023)
- Zawya (2022)
- European Parliament (2021)
- Wipro (2020)
- Morgan Lewis (2017)
- Deloitte (2016)
- Perficient (2016)




