Introduction: Cyber Threats, Powered by AI
In today’s digital landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a fundamental driver of transformation across all sectors, enabling a new era of efficiency and innovation. However, the very capabilities that make AI invaluable have given a rise to a new breed of cyber threats. For instance, according to a study conducted by Harvard Business Review, the rise of AI-automated phishing, accurately mimicking trusted sources, scored a 60% success rate in comparison to non-AI-phishing messages created by human experts.
As AI continues to evolve, so does the sophistication of these attacks, indicating the emergence of self-evolving threats that can adapt in real time to conventional security measures, and challenging the existing cybersecurity frameworks.
Understanding AI-Driven Cyber Threats
AI-driven cyber threats leverage AI to automate, accelerate, and innovate cyberattacks. Additionally, these attacks are capable of adapting and evolving over time to bypass detection methods, making them particularly challenging to defend against. By employing AI, attackers can effectively analyze vast datasets, identify vulnerabilities, and execute cyberattacks with higher precision and efficiency.
Characteristics
AI-powered cyber threats are distinguished by several key characteristics that enhance their effectiveness:

Source: CrowdStrike
The Many Faces of AI Cyber Threats
According to CrowdStrike, a leading cybersecurity firm, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a US Government agency, the most common AI-powered cyberattacks include:
1. AI-Driven Social Engineering Attacks
Incorporates the use of AI to research targets, develop personas, and create highly personalized communications. This includes phishing and deepfake attacks, where AI crafts messages, emails, or media designed to deceive
2. Merged Evasion and Adversarial Attacks
Focuses on manipulating AI model inputs to cause incorrect outputs or corrupting the model’s training data and architecture to undermine its integrity and effectiveness
3. AI-Enabled Ransomware
Uses AI to enhance the targeting and execution phases of ransomware attacks. AI capabilities allow the ransomware to identify valuable data, optimize encryption processes, and adapt its tactics based on defensive responses
4. Privacy Attacks
Focuses on exploiting vulnerabilities in AI systems to compromise user data privacy. Techniques include data reconstruction, membership inference, model extraction, and property inference, each aimed at extracting or deducing sensitive information from AI models or their training data
The Growing Concern
Recent surveys and reports reflect a significant consensus among professionals regarding the potential risks associated with AI-driven attacks: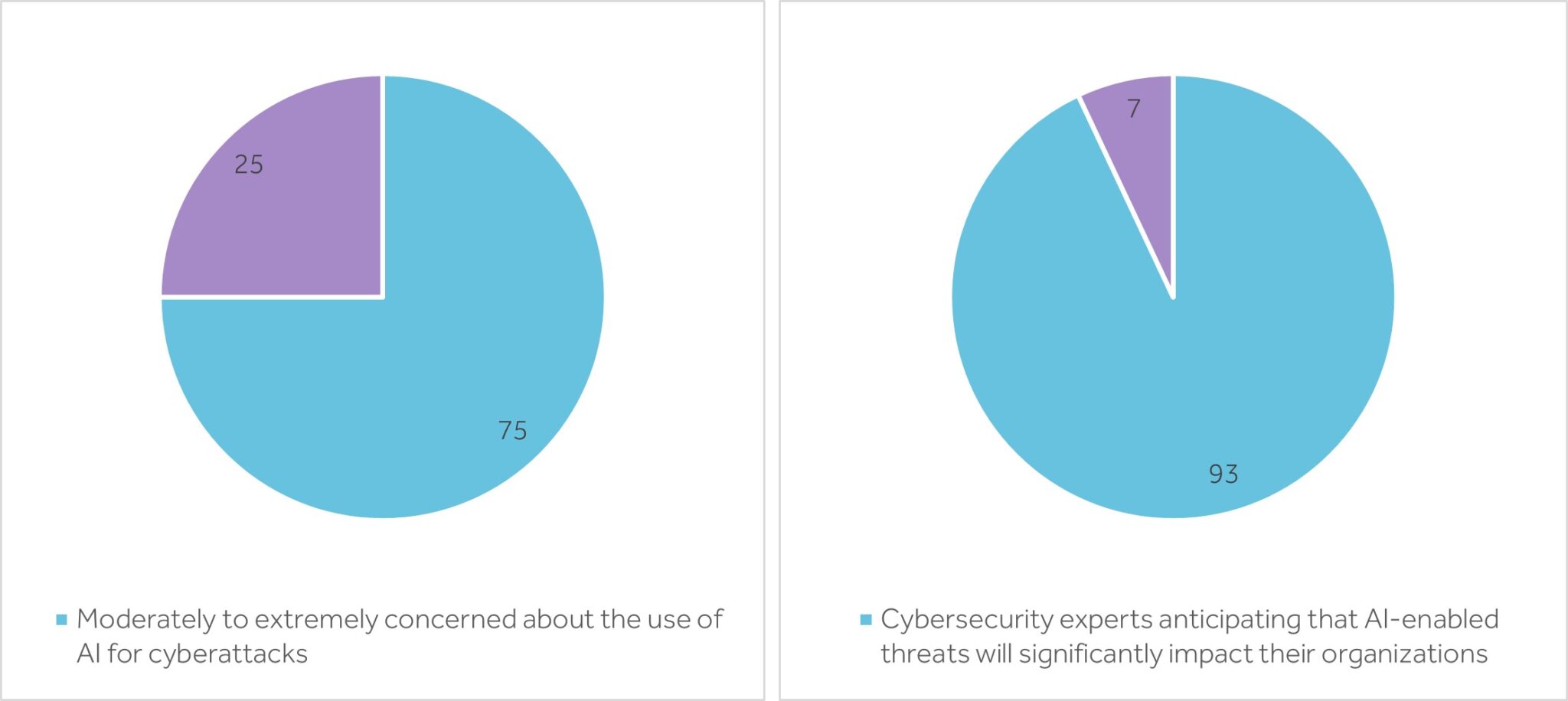 Source: ISC2, and CyberArk
Source: ISC2, and CyberArk
These statistics serve as a reminder of the growing concern among experts about the potential misuse of AI technologies in the cybersecurity realm. They underscore the critical need for enhanced protective measures, continuous education, and innovative solutions to stay ahead of AI-enabled threats.
Case Studies: A Closer Look
AI-driven threats are not just theoretical, as multiple cyberattacks have already occurred, demonstrating the significant impact of AI in cyberattacks.
In 2023, hackers bypassed the cryptocurrency company Bitfinex’s security by fooling its biometric system with deep-fake technology, injecting fake video and audio that mimicked legitimate users. This breach led to the theft of USD 150 Mn in cryptocurrencies. The incident underscores the critical vulnerabilities in biometric security, highlighting the need for more robust and multi-layered defense mechanisms.
Another notable incident occurred in 2019, involving the CEO of a UK-based energy firm who was misled into transferring USD 234,000 to the bank account of a Hungarian supplier by an AI-generated voice deepfake mimicking the voice of the parent company’s CEO, marking the first recorded instance of such technology used in fraud.
These examples highlight the evolving complexity of cyber threats powered by artificial intelligence, challenging traditional security measures and demanding more dynamic defenses.
The Difficulties of Guarding Against AI Cyber Threats
The integration of AI into cyber threats presents unique challenges that complicate the efforts of cybersecurity teams. These challenges stem from AI’s capabilities, which enhance the speed, complexity, and stealthiness of attacks.
-
Adaptability of AI Threats:
AI-driven threats can learn and adapt in response to countermeasures. This continuous evolution makes it difficult for static defense systems to keep up
-
Speed, Sophistication and Evasion:
AI accelerates cyberattacks, allowing them to quickly proliferate across networks, while simultaneously increasing their complexity. This enables more convincing phishing attempts and the creation of malicious content that can evade traditional security measures, making detection and response more challenging
-
Scalability:
With AI, cyberattacks can be conducted on a larger scale without a corresponding increase in human resources from the attacker’s side. This scalability makes AI-driven attacks a formidable challenge for any organization
- Detection and Response:
The strength of AI threats often requires equally sophisticated AI-driven security solutions. Implementing these advanced solutions can be costly and require specialized expertise
The Dual-Use Dilemma of AI
AI is widely used in cybersecurity to detect threats quickly, predict potential attacks, and automate tasks like network monitoring and incident response. However, it also empowers attackers by providing tools for rapid and scalable cyberattacks. This enables them to automate vulnerability discovery, execute attacks more efficiently, and craft highly convincing phishing emails by analyzing successful tactics. This dual-use nature of AI poses significant challenges, necessitating robust regulatory frameworks to ensure responsible usage and mitigate risks.
Conclusion: AI Fighting AI
As AI becomes more deeply integrated into the fabric of cybersecurity, it presents a battleground where AI is pitted against AI. On one side, advancements in AI are revolutionizing defensive capabilities, on the other, these same advancements equip attackers with powerful tools to create more complex, automated, and adaptive cyberattacks. This escalating arms race is evident as both sides harness AI’s potential to outpower each other. This ongoing conflict demands that future strategies not only react to but also anticipate the moves of an AI-empowered adversary, ensuring that defensive AI stays one step ahead in the ever-evolving cybersecurity chess game.
References:
- Harvard Business Review (2024)
- CrowdStrike (2024)
- ISC2 (2024)
- KPMG (2024)
- Deloitte (2023)
- CyberArk (2023)
- Forbes (2019)
Related articles

From Long Lessons to Microlearning: Rethinking How We Learn

AI for AI: Artificial Intelligence for Accessibility and Inclusion in Education


